end tidal co2 range in cardiac arrest
MEASURING END-TIDAL CO 2 LEVELS DURING CARDIAC ARREST Presentation for MSBI Nurses Prepared by Dr. Association between prehospital cpr quality and end-tidal carbon dioxide levels in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.

Abstract 223 End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Levels Predict Cardiac Arrest Circulation
There are approximately 50000 treated cardiac arrests each year in the UK with overall survival rate of less than 4.
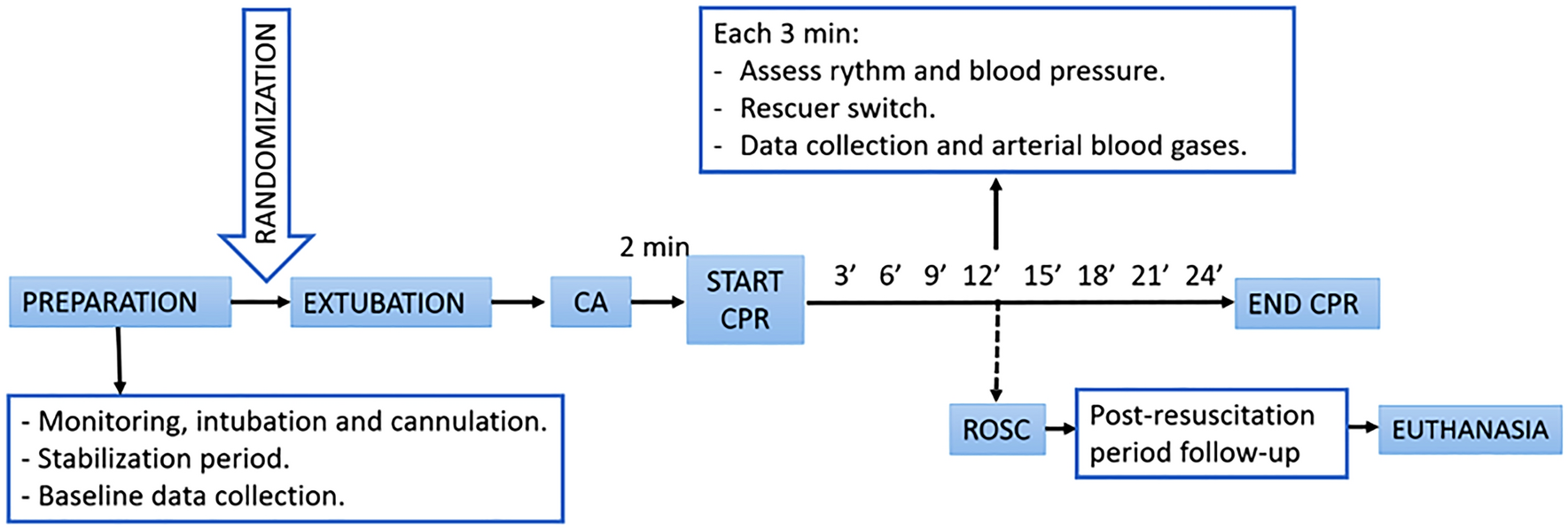
. Because it splits into CO2 and H20 So if rises after NaHCO3 do not. Increasing CO2 during CPR can also indicate the return of spontaneous circulation. End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring in cardiac arrest Acad Emerg Med.
This was a secondary analysis of a prospectively collected database on adult patients with OHCA who. In addition a decrease in the EtCO2 during resuscitative events of 25 was associated with a. A prospective observational study.
Measurement of end-tidal expiratory pressure of carbon dioxide ETCO 2 using capnography provides a noninvasive estimate of cardiac output and organ perfusion during cardiac arrest and can therefore be used to monitor the quality of CPR and predict return of spontaneous circulation ROSC. Bobrow MD Daniel W. Association between Prehospital CPR Quality and End-Tidal Carbon Dioxide Levels in Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Prehospital Emergency Care DOI.
Difference between asphyxial cardiac arrest and ventricular fibrillationpulseless ventricular tachycardia cardiac arrest. In clinical observational studies mean ETCO 2 levels in patients with ROSC are higher. 1031091090312720151115929 To link to.
BackgroundPhysiology 2 Monitoring end-tidal CO 2 ET-CO 2 provides instantaneous information about ventilation how effectively CO. Cardiac arrest is a common presentation to the emergency care system. Partial pressure of end-tidal carbon dioxide successful predicts cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the field.
Pierre Kory Laura OBrien RN CNS. CO 2 levels were significantly lower in cardiac arrest patients when compared with hypotensive patients 1 2 3 and 4 hours prior to a cardiac arrest see Table 1. End-Tidal CO2 as a Predictor of Cardiac Arrest Survival.
Cardiac Arrest Ryan A. Spaite MD Chengcheng Hu PhD Robyn McDannold MS Tyler F. A prospective observational study using a convenience sample.
Levine RL Wayne MA Miller CC. End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring in cardiac arrest. We aimed to identify distinct trajectories of end-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO 2 during cardiopulmonary resuscitation in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest OHCA and to investigate the association between EtCO 2 trajectories and OHCA outcomes.
If a patients heart stops and a patient goes into cardiac arrest end-tidal CO2 monitoring can help healthcare providers determine if chest compressions are being performed adequately. The purpose of this systematic review is to evaluate the prognostic value of ETCO2 during cardiac arrest and to explore whether ETCO2 values could be utilised as a tool to predict the outcome of resuscitation. Predicting likelihood of return of spontaneous circulation ROSC in that a persistently low ETCO2 tends to predict death whereas a high or rising ETCO2 is associated with a higher chance of ROSC.
Murphy RA Bobrow BJ Spaite DW et al. Also called capnometry or capnography this noninvasive technique provides a breath-by-breath analysis and a continuous recording of ventilatory status. In one of largest studies to date of prehospital capnography in cardiac arrest an initial EtCO2 10 mmHg 13 kPa was associated with an almost five-fold higher rate of return of spontaneous circulation ROSC.
Literature search was performed using Medline and EMBASE. The dynamic pattern of end-tidal carbon dioxide during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Although the normal range for CO2 should be.
Primary service area of an advanced life support ALS ambulance service including a city with a population of 70745 and the. An accurate early predictor of the outcome of resuscitation is needed. The global incidence of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest OHCA is estimated to be 28 to 44 cases per 100000 population annually According to the Pan Asian Resuscitation Outcomes Study PAROS Clinical Research Network 54 of the patients survived to hospital discharge and only 27 of the patients recovered favourable neurological function.
Kolar M Krizmaric M Klemen P Grmec S. Mean CO 2 values were significantly higher in normal patients when compared with those in patients who had a cardiac arrest 3018 493 vs. Murphy MD Bentley J.
Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and model estimates were generated using a repeated-measures categorical model with restricted maximum likelihood estimation and fully specified autoregressive covariance to assess the effect of. Because impaired circulation during arrest causes CO2 to build up in the bloodstream the initial ETCO2 reading may initially be higher than the normal 35-45 mm Hg range as it gets washed out of. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETco 2 monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance ventilation.
End-tidal carbon dioxide was collected from 5 to 2880 minutes before inhospital cardiac arrest. Lah K Križmarić M Grmec S. To assess the prognostic value of initial end-tidal CO2 pressures PETCO2 during CPR in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest OHCA.
1 The decision to terminate cardiopulmonary resuscitation CPR is often challenging to heath care providers mainly due to the lack of objective and clearly defined. PMC free article Google Scholar. End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring in cardiac arrest.
In fact its commonly called the ventilation vital sign. End tidal carbon dioxide CO2 correlates with cardiac output during cardiopulmonary resuscitation in cardiac arrest patients. Measuring end-tidal CO2 in cardiac arrest patients is helpful for.
CO2 will decrease prior to a cardiac arrest in patients that are intubated in an intensive care setting. Capnography can also let healthcare providers know if the patients heart starts working again on its own. End-tidal carbon dioxide and outcome of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.
End tidal CO2 in cardiac arrest.

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

Sar Helicopter Paramedic Practice Etco2 Measuring To Assist With Cpr Attempts Journal Of Paramedic Practice

The Impact Of Ventilation Rate On End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Level During Manual Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Resuscitation

Effects Of Airway Management And Tidal Volume Feedback Ventilation During Pediatric Resuscitation In Piglets With Asphyxial Cardiac Arrest Scientific Reports

The Use Of End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Etco2 Measurement To Guide Management Of Cardiac Arrest A Systematic Review Resuscitation

Average Etco2 Kpa During Cpr In Patients With Or Without Rosc Download Scientific Diagram

End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Etco2 And Ventricular Fibrillation Amplitude Spectral Area Amsa For Shock Outcome Prediction In Out Of Hospital Cardiac Arrest Are They Two Sides Of The Same Coin Resuscitation
End Tidal Co2 Monitoring In The Pre Hospital Environment More Than Just Endotracheal Tube Placement Confirmation Journal Of Paramedic Practice

Quantitative Waveform Capnography Acls Medical Training
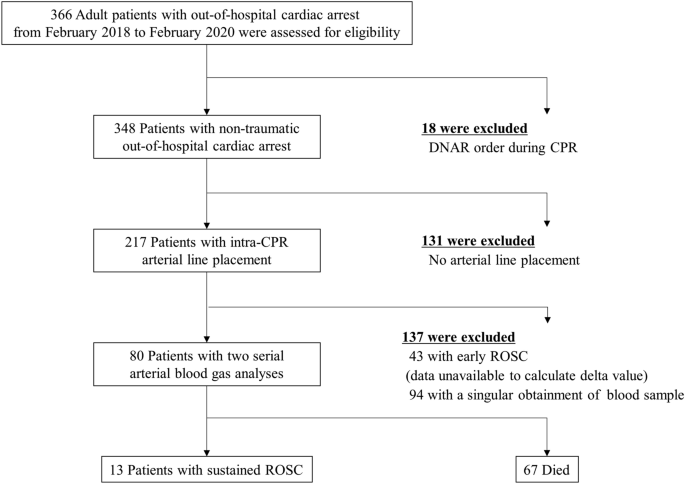
Dynamic Changes In Arterial Blood Gas During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation In Out Of Hospital Cardiac Arrest Scientific Reports

Use Capnography For A Patient In Cardiac Arrest Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

Pals Team Response Final Scenario Sophia Giamanti Complete Solution 2022 In 2022 No Response Nursing Questions Cardiac Rhythms
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project



